Health
Step-by-Step Guide to the Cell Therapy Manufacturing Process
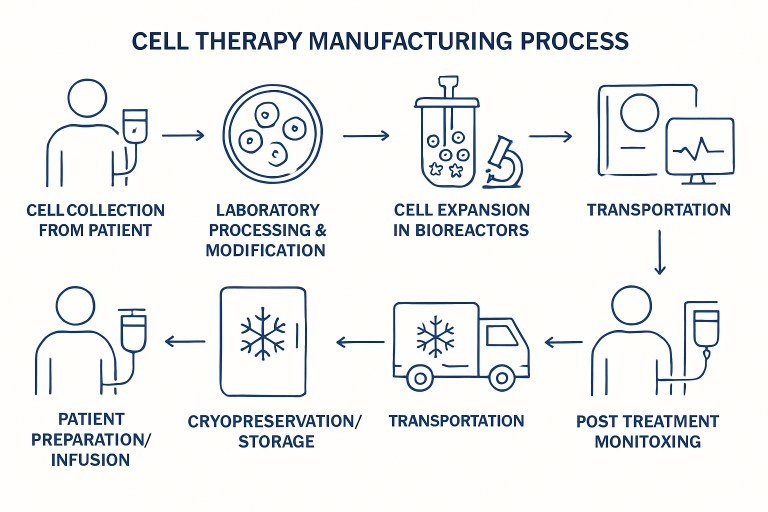
Cell therapy stands at the forefront of modern medicine, offering hope and revolutionary solutions for conditions once deemed incurable. This advanced method harnesses living cells—often derived from the patient—to treat illnesses ranging from cancer to autoimmune diseases. By understanding how cell therapy manufacturing works, patients, clinicians, and researchers can better appreciate the rigorous standards and innovations that ensure safe and effective treatment.
Unlike traditional drug therapies, cell therapy is tailored for each individual. Innovative manufacturing protocols are crucial for delivering quality and consistency amid the complexities of working with living cells. A reliable manufacturing process lays the groundwork for scalable, accessible, and lifesaving therapies that can turn medical possibilities into realities.
Patient Cell Collection
The process starts at the patient’s bedside or clinic, where specific cells are obtained—typically through a procedure called apheresis. During apheresis, blood is drawn from the patient, and cellular components such as T cells (critical for many immunotherapies) are separated and collected, while the remaining blood is returned to the patient. This vital step ensures that the right starting material is secured, as the journey from patient to therapy hinges on getting high-quality, viable cells.
Cell collection must be precisely timed and handled, as improper collection or delays can lead to cell degradation and negatively impact the success of the final therapy. Rigorous protocols and trained staff are crucial for maintaining optimal conditions from the outset.
Cell Processing and Modification
After collection, the journey continues in specialized laboratories, where the cells undergo initial processing to purify and isolate the desired cell types. Impurities and unwanted components are meticulously removed to prevent contamination or adverse reactions. Next, many advanced therapies, such as CAR-T cell therapy, involve genetic modification. In this phase, T cells are engineered to express new proteins that allow them to target specific disease markers (such as antigens on cancer cells). This genetic reprogramming is often accomplished using viral vectors or gene-editing technologies.
The processing and modification stage is a cornerstone of cell therapy’s therapeutic power. Precision, sterility, and careful monitoring remain critical, as errors at this stage could compromise the safety or effectiveness of the eventual product.
Cell Expansion
Having been modified, the now-potent cells require expansion to reach therapeutic doses. This process utilizes highly controlled bioreactors to nurture the cells, providing them with essential nutrients while maintaining optimal temperature, gas, and pH levels. The goal is to achieve the right cell count while maintaining function and potency. Cell expansion must be carefully monitored, as introducing contamination or over-expanding the cells could reduce their effectiveness and lifespan.
By achieving the proper cell population, manufacturers ensure that patients receive enough cells to mount a meaningful biological response against their disease.
Quality Control and Testing
Before being approved for patient delivery, expanded cells undergo a battery of quality assessments. Rigorous testing protocols confirm a wide range of product quality attributes, including cell identity (are these the correct cells?), purity (are they free from unwanted cell types?), potency (are the cells capable of performing their intended function?), and sterility (are they free from microbial contamination?). Every aspect must meet regulatory standards, ensuring the highest margin of safety.
Quality control is not simply a hurdle to clear before reaching the clinic—it is an embedded part of the culture in cell therapy manufacturing. Releasing a product that fails to meet established standards could put patients at serious risk, making this stage one of the most critical in the entire process.
Cryopreservation and Storage
With therapy approval, the viable cellular product undergoes cryopreservation—a process where cells are frozen at extremely low temperatures using specialized cryoprotectants. This critical step enables safe storage and convenient transport, often for days or weeks, without sacrificing cell integrity. Cryopreservation allows therapy providers to coordinate manufacturing with patient treatment schedules, expanding access across distances and healthcare networks.
Advanced techniques in cryopreservation are key to ensuring long-term stability. Inadequate freezing or thawing techniques can lead to cell damage, thereby diminishing the efficacy of the treatment.
Transportation to Treatment Facility
Once cryopreserved, the cellular medium is placed in validated shipping containers engineered to maintain ultra-low temperatures throughout the journey. Every minute outside this optimal range could harm the cells, so a reliable cold chain is maintained from the manufacturing facility to the clinical site. Secure, real-time monitoring and best-practice logistics are vital to guarantee that what leaves the laboratory is identical to what is received by the treating physician.
This dedication to safety underscores the precision and care underpinning the entire field of advanced therapies.
Patient Preparation and Infusion
Before receiving their personalized cell therapy, patients may require conditioning treatments such as chemotherapy or immunosuppression to optimize the environment for the infused cells. This step prepares the body, often by reducing existing immune cells that could hinder therapy, thereby improving efficacy. The prepared, thawed cellular product is then carefully infused into the patient via intravenous administration, completing the manufacturing journey and beginning the therapeutic phase.
Experienced clinicians must carefully manage infusion procedures to minimize risk and ensure the patient’s comfort and safety during this transformative step.
Post-Treatment Monitoring
After the infusion, meticulous follow-up is necessary to monitor for immediate side effects and assess the therapy’s effectiveness over time. Patients are regularly evaluated through clinical exams, blood tests, and imaging to detect potential adverse reactions, such as cytokine release syndrome or infection, and to assess the long-term effects of the treatment. These data are vital for refining future therapies and improving patient outcomes worldwide.
Continued research and feedback from post-treatment monitoring inform improvements to the entire cell therapy pipeline, creating a feedback loop of learning and advancement.
Final Thoughts
The cell therapy manufacturing process is a multi-faceted, highly controlled journey that converts a patient’s own cells into living medicines. Each step—from cell collection and modification, through rigorous testing and secure transport, to careful infusion and follow-up—is built upon stringent quality and safety protocols. This complexity reflects both the promise and responsibility of cell therapy: delivering lifesaving potential tailored to each individual, setting new standards for what’s possible in modern medicine.
Health
8 Points a Good Therapist Keep in Mind While Doing ADHD Therapy

Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects attention, impulse control, emotional regulation, and executive functioning. Effective ADHD therapy requires far more than generic advice or behaviour management. A good therapist approaches ADHD with empathy, structure, and a deep understanding of how the condition impacts both the individual and their environment.
8 Key Points A Skilled Therapist Must Keep in Mind While Doing ADHD Therapy
By keeping several key points in mind, a skilled therapist can create meaningful and lasting change for clients of all ages.
1. Understanding ADHD Beyond Stereotypes
One of the most important points a good therapist keeps in mind is that ADHD is not simply about hyperactivity or lack of focus. It presents differently in each individual. Some clients struggle primarily with inattention, others with impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, or executive dysfunction.
A competent therapist avoids stereotypes and takes time to understand the client’s unique challenges, strengths, and life context. This personalised understanding allows therapy to be more effective and respectful, reducing shame and self-blame.
2. Building a Strong Therapeutic Relationship
Trust and safety are essential in ADHD therapy. Many individuals with ADHD have experienced criticism, academic struggles, or repeated failures, which can damage self-esteem. A good therapist creates a non-judgmental environment where clients feel understood rather than blamed.
By validating experiences and acknowledging effort, therapists help clients feel motivated and engaged in the therapeutic process. A strong therapeutic alliance increases consistency and long-term commitment to therapy.
3. Setting Realistic and Achievable Goals
ADHD therapy near me is most effective when goals are practical and attainable. A skilled therapist avoids overwhelming clients with unrealistic expectations or too many changes at once. Instead, goals are broken down into manageable steps that fit the client’s daily life.
These goals may involve improving time management, reducing emotional outbursts, enhancing organisation skills, or strengthening relationships. Regularly reviewing and adjusting goals ensures therapy remains relevant and encouraging.
4. Focusing on Executive Function Skills
Executive functioning difficulties are central to ADHD. A good therapist focuses on building skills such as planning, prioritising, task initiation, and follow-through. Rather than simply telling clients what they “should” do, therapists provide structured strategies that work with the ADHD brain.
Tools like visual schedules, reminders, routines, and external supports are often introduced. Therapists also help clients identify which strategies work best for their individual needs.
5. Addressing Emotional Regulation and Self-Esteem
Emotional dysregulation is a commonly overlooked aspect of ADHD. Good therapists pay close attention to emotional responses such as frustration, anger, anxiety, or overwhelm. Therapy includes teaching clients how to recognise emotional triggers and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Equally important is rebuilding self-esteem. Many individuals with ADHD internalise years of negative feedback. A good therapist near me helps reframe these experiences, highlighting strengths and promoting self-compassion.
6. Involving Families and Support Systems
For children and adolescents, family involvement is essential in ADHD therapy. A good therapist works with parents or caregivers to ensure consistency between therapy sessions and home environments. Families are educated about ADHD so they can respond with understanding rather than punishment.
For adults, therapists may help clients improve communication with partners, employers, or educators. Support systems play a crucial role in reinforcing therapeutic progress.
7. Adapting Therapy to Developmental Stages
ADHD therapy should be developmentally appropriate. What works for a young child may not work for a teenager or adult. A skilled therapist adapts language, tools, and expectations based on the client’s age, responsibilities, and life stage.
This adaptability ensures therapy remains practical and relevant, supporting long-term success.
8. Monitoring Progress and Remaining Flexible
ADHD therapy is not a one-size-fits-all process. A good therapist regularly evaluates progress and remains flexible. If a strategy is not working, it is adjusted rather than forcing the client to conform to an ineffective approach.
This flexibility demonstrates respect for the client’s experience and encourages collaboration rather than compliance.
Conclusion
A good therapist approaches ADHD therapy with empathy, structure, and adaptability. By understanding the condition deeply, building strong relationships, setting realistic goals, and addressing both practical and emotional challenges, therapists create a supportive path toward growth. Keeping these points in mind allows ADHD therapy to empower individuals, strengthen families, and improve overall quality of life.
Health
The Role of Genetic Testing After IVF Failure

Genetic testing offers diagnostic insights for you and your healthcare provider after an IVF failure. Identifying underlying factors assists healthcare professionals in creating a treatment plan or in choosing whether to try another cycle. Here is more information about the role of genetic testing after IVF failure:
Understanding Embryo Potential
Genetic testing of embryos evaluates whether they are chromosomally normal and suitable for transfer or long‑term development. Embryos with incorrect chromosomal configurations may be associated with failed implantation, miscarriage, or later developmental issues. DNA testing functions as a structured report available to doctors on embryos with developmental potential, supporting the selection of candidates for implantation.
Detecting Endometriosis and Endometritis
Testing can show whether endometrial tissue is growing abnormally outside the uterus. This tissue blocks implantation by altering the pelvic and uterine environment. Endometriosis can reduce fertility without causing prominent symptoms. While it occurs outside the uterus, it has the potential to disrupt endometrial receptivity and interfere with blastocyst implantation. Women, including those with mild or asymptomatic endometriosis, may have an elevated risk of miscarriage. Genetic testing helps detect situations that might have contributed to IVF failure.
Endometritis testing evaluates inflammation in the uterine lining. Because endometritis can disrupt the uterine environment required for embryo implantation and pregnancy, testing focuses on identifying inflammatory changes in endometrial tissue. The results help physicians determine whether treatment is needed to eliminate infection or inflammation, and this information supports more precise, fertility-focused care.
Identifying Progesterone Resistance
Testing may detect if cells resist progesterone, limiting their ability to prepare the uterine lining for pregnancy. The chances of a failed implantation or unstable pregnancy may increase when this hormonal resistance contributes to an abnormal endometrial lining. Insufficient or absent progesterone responsiveness is reported in approximately two‑thirds of infertility cases in women with endometriosis. Other issues might arise with hormonal treatment, as it may not be able to correct this abnormality. Genetic testing that uncovers such resistance factors provides information for developing intervention measures targeted to this pattern.
Analyzing CD138 Marker and BCL6 Marker
The BCL6 gene is expressed in response to inflammatory activity and is strongly associated with endometriosis. Elevated levels of this marker often reflect an increased inflammatory response that creates a less receptive uterine environment for implantation. By identifying BCL6 expression patterns, physicians are able to tailor treatment strategies to address inflammation more precisely. BCL6 marker testing assists clinicians in evaluating cases of unexplained infertility in which inflammation plays a contributing role.
Elevated CD138 levels indicate chronic inflammation within the uterus and are frequently associated with impaired embryo implantation. Inflamed endometrial tissue does not support the conditions required to establish or sustain a pregnancy. A CD138 marker test identifies inflammatory patterns linked to implantation failure, recurrent pregnancy loss, or missed pregnancies, and these findings guide targeted clinical intervention. This information supports the detection and treatment of persistent infections that compromise uterine function. Following successful treatment, uterine inflammation is reduced, and the endometrial environment becomes more supportive of stable embryo implantation.
Understanding Treatment Solutions
Doctors use genetic and molecular test results when deciding whether to perform a laparoscopy to remove endometriotic implants, scar tissue, or adhesions that can interfere with reproduction. Removal of affected tissue helps the uterus develop a more receptive lining for implantation during IVF cycles. When physicians know which areas require treatment, they can plan interventions more precisely and effectively. Findings from genetic testing may also highlight signs of endometriosis, guiding further clinical decision-making. In these cases, laparoscopic procedures offer diagnostic confirmation and complement genetic test results.
Testing for endometriosis identifies inflammatory and hormonal patterns that physicians can address before initiating another IVF cycle. Because hormonal suppression therapy lowers estrogen levels, it helps stabilize the uterine environment while also reducing pain symptoms. The therapy is used to shrink endometrial growths and slow the progression of endometriosis-related tissue changes, and it limits further tissue proliferation within the endometrium. By reducing hormone-driven inflammation, treatment supports conditions necessary for embryo implantation and the maintenance of pregnancy.
Contact Healthcare Providers After IVF Failure
Testing for potential genetic or uterine factors after failed in vitro fertilization cycles helps identify underlying causes and possible treatment paths. A physician’s expertise and advanced testing provide structured information to guide next steps after an IVF failure. Work with fertility experts today.
Health
What Endometriosis Tests Reveal About Your Health
An endometriosis test helps detect abnormalities, such as inflamed pelvic structures and endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus. Getting tested soon after noticing signs like worsening menstrual pain allows for early intervention and prevention of disease progression. Here are a few things that endometriosis tests can reveal about your health:
Pelvic Exam
A pelvic exam serves as an initial, non-invasive assessment of the pelvic structure when you report symptoms related to endometriosis. It helps diagnostic service providers get real-time insights into the physical condition of:
- Uterus
- Ovaries
- Cervix
- Fallopian tube
This endometriosis test begins with a visual assessment of the external genitalia, and then progresses to gentle internal palpation. A pelvic exam may contribute to earlier identification of endometriosis by allowing for clinical findings that raise suspicion and help guide further evaluation. During the exam, a clinician assesses for areas of pelvic tenderness. In the bimanual portion of the exam, the provider applies pressure to the pelvic organs to evaluate for tenderness or other abnormalities.
Localized pain may suggest active inflammation that requires immediate intervention. Internal palpation detects larger growths or cysts in the ovaries, and this outcome helps direct further imaging tests. Reduced uterine movement during palpation can suggest a fixed uterus and adhesions, which contribute to infertility. Other endometriosis-related issues this exam helps reveal include abnormal tissues or lesions in the cervix and uterosacral nodularity.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
An MRI can be used to evaluate suspected endometriosis by producing detailed images of pelvic anatomy. It uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate high-resolution images. It is particularly useful for assessing deep-infiltrating endometriosis and involvement of structures such as ligaments and connective tissue. MRI provides superior soft-tissue contrast compared with ultrasound, which helps identify findings that may not be visible on other tests. An MRI is a safe endometriosis test since it involves no radiation exposure; this makes it a suitable choice for repeated use in reproductive-age women.
This imaging modality can help identify ovarian endometriomas, which may appear as well-defined cystic lesions with characteristic signal patterns on imaging. These findings inform fertility counseling and treatment planning. MRI is also useful for assessing deep infiltrating endometriosis involving pelvic organs, such as the bladder, and for evaluating associated changes like adhesions or fibrosis that may distort pelvic anatomy.
Biomarker Blood Tests
A blood test identifies specific biomarkers in the bloodstream that indicate the presence of endometriosis. Some of the biomarkers analyzed through this specialized diagnostic procedure include:
- Proteins
- Hormonal factors
- Genetic markers
- Inflammatory molecules
A testing service provider draws a blood sample and then sends it to a specialized lab for analysis. A biomarker blood test may reveal issues related to endometriosis by showing abnormal tissue activity or inflammation. Changes in some blood markers, such as elevated hormonal levels, help providers determine causes of endometriosis-related symptoms like menstrual irregularities and pain.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy, a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure, provides definitive confirmation of endometrial-like tissue growth outside the uterus when lesions are directly visualized. This procedure allows surgeons to take small tissue samples and analyze them in the laboratory to support diagnosis and treatment planning. Laparoscopy can be helpful when imaging studies, such as MRI or ultrasound, are inconclusive. It enables providers to identify ovarian endometriomas and assess their potential impact on reproductive function. Laparoscopy also provides insight into the extent of adhesions and scar tissue within the pelvis.
Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS)
A transvaginal ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the reproductive organs. The test provides real-time imaging, allowing the provider to observe pelvic structures and their movement during the examination. Transvaginal ultrasound is a commonly used, noninvasive imaging method in routine gynecologic evaluations. Because it does not involve ionizing radiation, it is safe for repeat use when clinically indicated.
A transvaginal ultrasound helps identify ovarian endometriomas, which inform cyst evaluation and further management. It may also demonstrate features such as the pouch of Douglas obliteration, which can be associated with pelvic adhesions or advanced endometriosis. Transvaginal ultrasound allows for the assessment of ovarian morphology, including the presence and number of follicles. This contributes to the overall evaluation of ovarian function.
Get an Endometriosis Test Today
An endometriosis test helps identify signs like scar tissue or ovarian cysts at an early stage, and this allows for more personalized treatment options. Advanced women’s health diagnostic services include targeted tests for infertility and pelvic pain to promote accurate results and effective treatment plans. Contact a reputable diagnostic provider today to begin your testing.
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoYourAssistantLive com: The Future of Smart Digital Assistance
-

 food4 months ago
food4 months agoCalamariere: How to Perfectly Prepare at Home
-

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months agoBaddi Hub: An Emerging Industrial and Business Hotspot
-

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months agoSimpcit6: Redefining Simplicity in a Complex World
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNerovet AI Dentistry: Enhancing Patient Experience and Treatment Outcomes Dental Care
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoVoomixi com: The Digital Platform Redefining Online Interaction
-

 Crypto4 months ago
Crypto4 months agoCrypto30x.com vs Other Crypto Sites – Best Bitcoin Tools?
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPyjamaspapper: The Ultimate Blend of Comfort and Style in Sleepwear
